Table of Contents
The concept of prepaid expenses can be explained by the activity of paying upfront for goods or services that one rent and receive later over time. For instance, renting an apartment or paying for car insurance. Businesses do this all the time, and they must follow accounting rules. This is because that prepayment is an asset having value beyond the present time. As a result, businesses use prepaid expense amortization as a way to spread prepaid expenses over the accounting periods in which the business can derive value from them.
Streamline Your Accounting Closure with Automated Amortizations in NetSuite
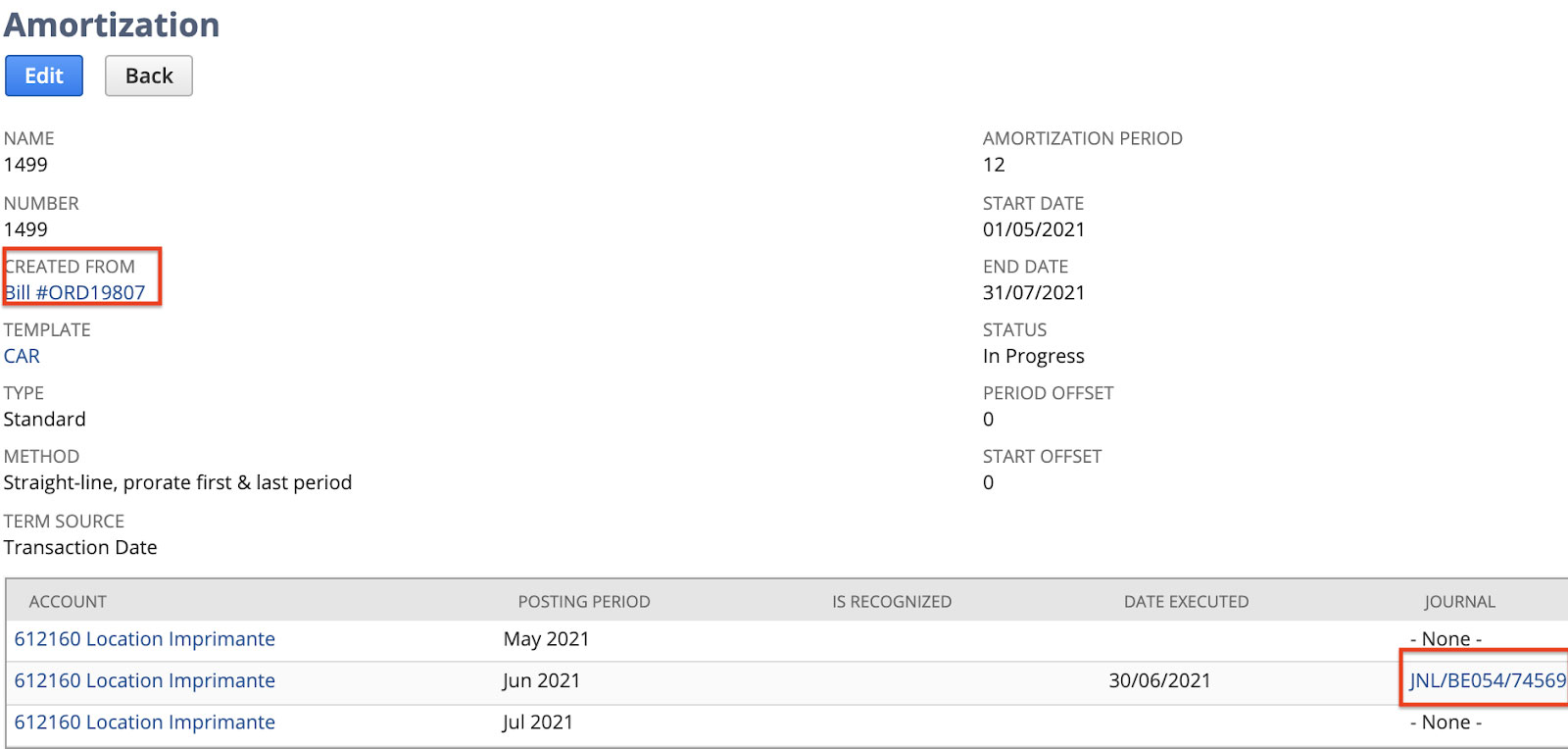
Prepaid expenses are common for businesses of all types, sizes, and industries. However, they maintain prepaid expenses and their related amortization schedules. For the most part, it becomes tedious and time-consuming when done manually, in spreadsheets. Here, leveraging Prepaid Expense Amortization Software such as NetSuite Financial Management automates the steps involved with amortizing prepaid expenses to streamline the accounting close.
Prepaid Expense Amortization software helps maintain a register for every prepayment, create the related amortization schedule, and automate the adjusting journal entries for the entire lifecycle of the prepaid expense asset. This drives more efficiency and accuracy across business’s accounting while increasing visibility for internal stakeholders via NetSuite’s drill-down functionality. Notably, service-oriented businesses can avail of NetSuite field service management as well.
What Are Prepaid Expenses?
A prepaid expense is an asset or prepaid asset that is generated when a business pays for a product or service before receiving it. Businesses often come across upfront payments, such as for rent, insurance, legal services and more. Sometimes businesses prepay as a term of the business transaction and other times opt to pay in advance to capture discounts. This is also called prepay discounts.
Prepaid expenses are paid and recorded before they deliver value to the business. To be GAAP-compliant, businesses record the prepaid expenses assets and amortize them. Many businesses write them over time by directly crediting the asset accounts and debiting the related expense accounts over the period that the prepayment gives benefits to the business.
For the most part, the bookkeeping for prepayments is easy for businesses that use cash-basis accounting. It involves simply recording the entire amount as an expense when the cash is paid. However, it can hard on the business’s income statement, as the entire expense hits all in one period. This potentially causes confusing swings in profitability. Hence, accrual basis accounting needs a different approach. Here, the prepayment is capitalized as an asset and then amortized. Although the approach is a bit more complicated, better reflects the expense in the periods the expense will cover.

Key Takeaways
- When you amortize the prepaid expense it matches expenses to the right period in accordance with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP).
- Each prepaid expense is unique as per its underlying transaction and needs proper analysis to create an appropriate amortization schedule.
- The right accounting software helps maintain a prepayment register, generate the related amortization schedules and automate the adjusting journal entries.
- Prepaid Expense Amortization helps make the accounting close more efficient and less susceptible to error.
Close Faster with Cloud Accounting
Businesses can simplify their prepaid expense amortization process with our free guide on NetSuite cloud accounting.
Types of Prepaid Expenses
Businesses often prepay many types of expenses. For the most part, the prepaid expense represents an asset to an organization because it has future economic value. However, the asset is classified on the balance sheet and the method used to amortize it varies depending on the period for which value is received and the type of the transaction.
Additionally, prepaid expenses expected to be used up within one fiscal year are reflected as current assets on a balance sheet. For the most part, it comes with NetSuite accounting support and affects the working capital of a business organization. Prepaid expenses spanning multiple years are considered long-term prepaid assets.
Rent
Property owners often need renters to make cash payments in full at the beginning of a rent agreement. For the renting business, this advance payment is considered a prepaid expense. This is because it has not yet taken the space for the entire time covered by the payment. For example, an annual rental agreement may be paid in a single installment in January, causing the remaining 11 months to be set up as a prepaid rent asset.
Insurance
Insurance premiums are often structured in 6-or 12-month coverage periods that are paid in advance. When the payment is made, the premium reflects a prepaid expense for the policyholder. This is because they have not yet received the insurance coverage for the entire period. For the most part, a prepaid insurance asset is valued as the prorated portion of the unexpired insurance premium.
Advertising
The cash a business pays for an advertising campaign yet to begin or is still running is considered a prepaid expense for the advertiser. It is reflected as an asset on its balance sheet. Prepayment is commonly needed in order to reserve advertising space. However, the expense should be recognized when the ads run and not when they are paid. A prepaid advertising expense reflects as an asset on the balance sheet until that time.
Other
Prepayments are quite common in business and there are many other types. The details of each situation are unique.
However, the accounting follows the same three-step pattern
- Make an Advance Payment
- Establish an Asset For The Prepaid Expense
- Amortize it Over The Period Of Consumption
Some examples of other prepaid expenses are
- Subscriptions
- Professional Services Fees
- Supplies
- Software Licenses
- Maintenance Contracts
- Taxes And Utilities
As it is impossible to include a comprehensive list of every possible prepaid expense, it is more useful to understand the concept in order to identify transactions creating prepaid expense assets.
Amortization of Prepaid Expenses in Business Accounting
Prepaid Expense Amortization, rather than expensing it all at, makes financial statements for small businesses and even large enterprises more accurate. For the most part, amortization is the method for apportioning payments over the fiscal periods. In this fiscal period, they have an impact and a requirement for compliance with accounting’s matching principle. As a practical matter, amortization makes financial statements more comparable from period to period by streamlining large swings that would be caused by the timing of payments.
Why inoday for NetSuite Accounting Solutions?
At inoday, a certified and #1ORACLE NetSuite Channel Partner, you can connect to our accredited and certified NetSuite Consultants. These experts are globally acclaimed for delivering 16+ years of experience in driving Digital Transformation via Cloud Computing Solution and rendering extensive support even beyond the implementation lifecycle ensuring business continutiy.
We are adept at delivering custom-made solutions to meet unique requirements and take an out-of-the-box approach to solve bottlenecks and that too, within the stipulated time.
FAQs
What is NetSuite for accounting?
NetSuite cloud accounting software simplifies the process of recording transactions. For the most part, NetSuite accounting manages payables and receivables, collects taxes, and helps in closing the books. Also, it enables timely, accurate reporting, and greater control of financial assets.
Is NetSuite good accounting software?
Oracle NetSuite is one of the leading solutions in the field of ERP. This multifaceted solution expedites an organization’s financial transactions. These transactions include accounts receivable and payable, as well as keep track of a company’s compliance obligations.
How do you amortize prepaid expenses?
To properly amortize a prepaid asset in the most basic calculation, the business divides the total value of the prepaid expense by the number of months it will last.
For more details on Prepaid Expense Amortization, write to us at info@inoday.com Or Schedule A Demo








